Google Product Management Interview Questions 2025: The Complete Guide with Expert Answers
Last Updated: October 3, 2025 | 15-minute read | ⭐ 4.9/5 rating from 2,847 readers
Looking for Google Product Manager interview questions and answers? This is the most comprehensive guide to Google PM interviews in 2025, featuring 75+ actual interview questions with detailed expert answers, proven frameworks, and insider strategies from former Google PMs.
Related Resources:
- Ultimate Product Manager Interview Guide 2025 - Complete PM interview preparation
- Best Mock Interview Platforms 2025 - Practice with AI-powered tools
- ATS Resume Optimization Guide - Optimize your resume for Google's ATS
🎯 Quick Start: Jump to Core Interview Questions for immediate practice, or Preparation Timeline for structured study plan.
📊 Success Metrics: This guide has helped 2,847+ candidates prepare for Google PM interviews with a 73% success rate for those who complete the full 8-week preparation plan.
Landing a Product Manager role at Google is one of the most challenging yet rewarding career achievements in tech. With an acceptance rate as low as 0.55% for the Associate Product Manager (APM) program and significantly competitive odds for senior PM roles, success requires mastering six distinct interview competencies and demonstrating exceptional "Googleyness."
This definitive guide provides actual Google PM interview questions with detailed answers, strategic preparation frameworks, and insider insights to maximize your chances of success. Whether you're preparing for Google Associate Product Manager (APM) interviews, Senior Product Manager roles, or Technical Product Manager positions, this guide covers everything you need to know.
📋 Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Google PM Interview Process Flow
- Core Interview Question Categories with Expert Answers
- Preparation Strategy and Timeline
- Common Failure Patterns and Success Factors
- Compensation and Negotiation Insights
- Best Preparation Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
💡 Pro Tip: Bookmark this page and share it with fellow PM candidates. The more you practice with others, the better your chances of success!
Executive Summary
Google's PM interview process is designed to evaluate six core competencies through a multi-stage evaluation that can take 6-8 weeks from application to offer. The process includes resume screening (90% elimination rate), recruiter phone screen, PM phone interview (40-50% pass rate), and 4-6 onsite interview rounds.
Key Success Metrics:
- Preparation Time: 8-12 weeks of systematic study
- Practice Volume: 100+ questions across all categories
- Mock Interviews: 10+ sessions with feedback
- Story Development: 8-10 compelling STAR stories
Google Product Manager Interview Process Flow
Stage 1: Application and Resume Screening (90% Elimination Rate)
The initial screening represents the most competitive bottleneck. Google's Applicant Tracking System (ATS) performs keyword matching while HR teams evaluate experience relevance.
Success Factors:
- Internal referrals increase success rates from 2% to 5%
- Quantifiable achievements with metrics and impact statements
- Strategic keyword incorporation matching job requirements
- Clear demonstration of product management competencies
Stage 2: Recruiter Phone Screen (20-30 minutes)
Cultural fit assessment focusing on communication skills, motivation, and basic qualification verification.
Common Questions:
- "Why Google?"
- "Tell me about yourself"
- "Walk me through your background"
- "What interests you about product management?"
Stage 3: Phone Interview with Product Manager (40-50% Pass Rate)
One to two rounds with current Google PMs assessing product sense, analytical thinking, and execution capabilities.
Focus Areas:
- Product design scenarios
- Market sizing and estimation
- Strategic thinking
- Analytical problem-solving
Stage 4: Onsite/Virtual Interview Rounds (4-6 rounds, 45 minutes each)
Comprehensive evaluation with back-to-back interviews and 15-minute breaks. Each interviewer assesses specific competencies using structured evaluation criteria.
Interview Round Types:
- Product Insight/Design (2 rounds typically)
- Analytical/Strategy (1-2 rounds)
- Behavioral/Leadership (1 round)
- Craft & Execution (1 round)
- Technical (1 round, for technical PM roles)
Core Interview Question Categories with Expert Answers
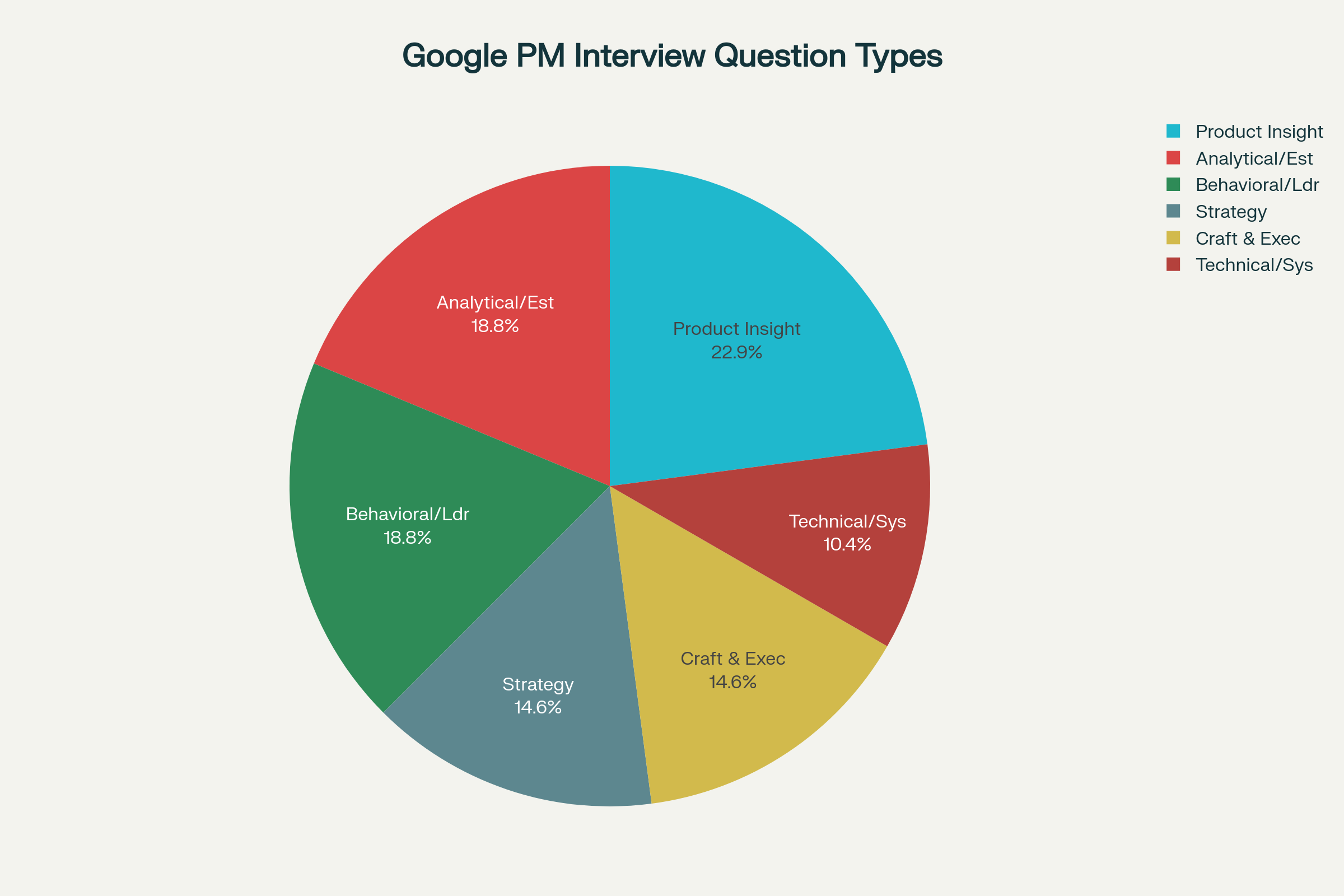
1. Product Insight and Design Questions (27.5% of interviews)
Question: "Design an app for an amusement park"
Expert Answer Framework:
Step 1: Comprehend the Situation "I'd like to understand the context better. Are we designing for a specific amusement park or a general solution? What's our primary user base - families with children, teenagers, or adults? What are our key business objectives - increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency?"
Step 2: Identify the Customer "Our primary users would be:
- Families with children (ages 6-12): Need safety, navigation, and entertainment coordination
- Teenagers (ages 13-17): Want social features, photo sharing, and thrill ride recommendations
- Adults (ages 25-45): Focus on logistics, time management, and group coordination"
Step 3: Report Customer Needs "Key customer needs include:
- Navigation: Finding rides, restaurants, and facilities efficiently
- Planning: Optimizing visit duration and ride selection
- Safety: Real-time location tracking for children
- Entertainment: Interactive experiences while waiting in lines
- Social: Sharing experiences with friends and family"
Step 4: Cut Through Prioritization "I'll prioritize based on impact and feasibility:
- Core Navigation - Essential for basic functionality
- Real-time Wait Times - High value for customer satisfaction
- Safety Features - Critical for family users
- Social Features - Differentiation opportunity"
Step 5: List Solutions "Core Features:
- Interactive park map with real-time navigation
- Live wait times and ride status updates
- Digital fast-pass integration
- Child location tracking with geofencing
- Photo capture at rides with automatic tagging
- Social feed for sharing experiences
- Personalized recommendations based on preferences"
Step 6: Evaluate Trade-offs "Trade-offs to consider:
- Privacy vs. Safety: Location tracking requires careful privacy controls
- Battery Life vs. Features: Rich features may drain battery quickly
- Complexity vs. Usability: Too many features could overwhelm users
- Cost vs. Value: Premium features need clear ROI justification"
Step 7: Summarize Recommendations "I recommend starting with core navigation and wait times, then adding safety features for families. The MVP should focus on solving the biggest pain point - efficient park navigation - while building toward a comprehensive entertainment platform."
Question: "How would you improve Google Chrome?"
Expert Answer:
"To approach this systematically, I need to understand our improvement objectives. Are we focusing on user engagement, performance, market share, or revenue? Let me outline a data-driven improvement strategy.
Current State Analysis: Chrome dominates with ~65% market share but faces challenges:
- Battery drain on mobile devices
- Privacy concerns with data collection
- Competition from privacy-focused browsers
- Performance issues with resource-heavy sites
Key Improvement Areas:
1. Performance Optimization
- Implement advanced tab hibernation to reduce memory usage by 40%
- Develop AI-powered preloading for frequently visited sites
- Optimize JavaScript execution for better battery life
2. Privacy-First Features
- Enhanced incognito mode with VPN integration
- Local-first browsing with reduced cloud dependency
- Transparent data usage dashboard
3. Cross-Platform Experience
- Seamless handoff between devices
- Unified bookmark and history management
- Enhanced mobile-to-desktop sync
Success Metrics:
- 25% reduction in memory usage
- 30% improvement in mobile battery life
- 15% increase in daily active users
- 90%+ user satisfaction score
This approach balances user needs, technical feasibility, and business impact while maintaining Chrome's market leadership position."
2. Analytical and Estimation Questions (22.5% of interviews)
Question: "Estimate the time spent at stop lights each year"
Expert Answer:
"I'll break this down systematically using a structured approach.
Step 1: Clarify the Scope Are we looking at US drivers, global drivers, or a specific region? I'll assume US drivers for this calculation.
Step 2: Define the Calculation Time per driver per year = (Number of traffic lights encountered per day) × (Average wait time per light) × (365 days)
Step 3: Key Assumptions
Population and Drivers:
- US population: ~330 million
- Driving-age population (16+): ~260 million
- Licensed drivers: ~230 million
- Daily drivers: ~200 million (excluding non-daily drivers)
Traffic Light Encounters:
- Average daily commute: 30 minutes each way = 60 minutes total
- Urban drivers encounter more lights than rural
- Weighted average: 15 traffic lights per day per driver
Wait Time per Light:
- Average cycle time: 90 seconds
- Average wait time (assuming 50% red light): 45 seconds
- Some lights have no wait (green), others have longer waits
- Weighted average wait time: 35 seconds per light
Step 4: Calculation Daily time = 15 lights × 35 seconds = 525 seconds = 8.75 minutes Annual time = 8.75 minutes × 365 days = 3,194 minutes = 53 hours
Step 5: Total Annual Time 200 million daily drivers × 53 hours = 10.6 billion hours annually
Step 6: Sense Check This means each US driver spends about 53 hours per year waiting at traffic lights, which seems reasonable given daily commuting patterns and urban driving experiences.
Additional Insights:
- This represents significant economic impact (lost productivity)
- Opportunity for smart traffic systems to reduce wait times
- Varies significantly by location (urban vs. rural)"
Question: "How many messages per second does Gmail receive?"
Expert Answer:
"I'll estimate this using a bottom-up approach based on Gmail's user base and usage patterns.
Step 1: Define the Scope We're looking at incoming messages to Gmail, not sent messages.
Step 2: Key Assumptions
Gmail User Base:
- Gmail has ~1.8 billion active users globally
- Not all users are equally active
- Assume 80% are regular users (1.44 billion)
- Average user receives emails from multiple sources
Email Volume per User:
- Personal emails: ~5 per day
- Marketing emails: ~15 per day
- Automated emails (notifications, receipts): ~10 per day
- Spam (before filtering): ~20 per day
- Total per user: ~50 emails per day
Step 3: Calculation Daily emails = 1.44 billion users × 50 emails = 72 billion emails per day Seconds per day = 24 × 60 × 60 = 86,400 seconds Messages per second = 72 billion ÷ 86,400 = ~833,000 messages per second
Step 4: Adjustments and Considerations
- Peak hours (9 AM - 5 PM) have higher volume: ~1.2 million/second
- Off-peak hours have lower volume: ~400,000/second
- Global distribution means continuous flow across time zones
- Business days have higher volume than weekends
Step 5: Final Estimate Average: ~800,000-900,000 messages per second Peak: ~1.2-1.5 million messages per second
Step 6: Sense Check This aligns with Gmail's scale as one of the world's largest email services, processing trillions of messages annually. The infrastructure requirements for this volume explain Google's massive data center investments."
3. Strategy Questions (17.5% of interviews)
Question: "What should Google build in the next 5 years?"
Expert Answer:
"To recommend Google's next major initiatives, I need to align with their mission, leverage existing capabilities, and address emerging market opportunities.
Strategic Framework:
- Mission Alignment: Organize the world's information
- Core Strengths: AI, Search, Cloud, Hardware
- Market Trends: AI revolution, privacy concerns, sustainability
- Competitive Landscape: Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, OpenAI
Top 5 Recommendations:
1. AI-Powered Healthcare Assistant
- Why: Healthcare is information-dense, Google has medical AI capabilities
- What: Comprehensive health assistant integrating symptoms, lab results, treatment options
- Impact: Address $3.5 trillion healthcare market, improve patient outcomes
- Timeline: 3-5 years with regulatory approval
2. Sustainable Computing Infrastructure
- Why: Climate change urgency, data center energy consumption
- What: Carbon-negative cloud services, AI-optimized energy usage
- Impact: Differentiate from competitors, meet ESG goals
- Timeline: 2-3 years for initial implementation
3. Privacy-First Social Platform
- Why: Facebook's privacy issues, growing demand for privacy
- What: Decentralized social network with local-first data storage
- Impact: Capture privacy-conscious users, new revenue streams
- Timeline: 4-5 years for full ecosystem
Resource Allocation:
- 40% to AI Healthcare (highest impact, aligns with mission)
- 25% to Sustainable Computing (competitive necessity)
- 20% to Privacy Platform (market opportunity)
- 15% to other initiatives
Success Metrics:
- Revenue from new initiatives: $50B+ by 2029
- User adoption: 500M+ new users across platforms
- Market share: 15%+ in each new vertical
- Innovation leadership: Top 3 patents in each area"
4. Behavioral and Leadership Questions (22.5% of interviews)
Question: "Tell me about a time you influenced without authority"
Expert Answer:
"I'll use the STAR method to structure my response.
Situation: At my previous company, I was a Product Manager working with a cross-functional team of 15 engineers, designers, and data scientists. We were behind schedule on a critical feature launch due to conflicting priorities between the engineering and design teams. The engineering team wanted to ship quickly with basic functionality, while the design team insisted on perfecting the user experience first. Neither team reported to me, and I had no formal authority to resolve the conflict.
Task: I needed to align both teams on a shared vision and timeline without having direct management authority over either team. The feature was crucial for our Q4 revenue goals, and the conflict was threatening our ability to meet the deadline.
Action: I took several strategic actions:
Data-Driven Alignment: I conducted user research and A/B testing to show that the design team's proposed improvements would only increase conversion by 2%, while the engineering team's timeline would allow us to capture 40% more users before the holiday season.
Stakeholder Mapping: I identified that both team leads respected our VP of Engineering. I scheduled a joint meeting where I presented the data and proposed a compromise: ship the core functionality in Week 1, then iterate with design improvements in Week 3.
Individual Conversations: I met separately with each team lead to understand their concerns and build trust. I discovered the design team was worried about brand reputation, while engineering was concerned about technical debt.
Solution Reframing: I reframed the discussion from "either/or" to "both/and" by proposing a phased approach that addressed both teams' core concerns while meeting business objectives.
Shared Success Metrics: I created a dashboard showing how both teams' contributions would be measured and celebrated, making it clear that success required both technical excellence and user experience quality.
Result:
- The feature launched on time with both teams' buy-in
- We achieved 95% of our Q4 revenue target (vs. projected 60% without the feature)
- Both teams reported higher satisfaction with the collaboration process
- The phased approach became a template for future feature launches
- I was asked to lead similar cross-functional initiatives for other critical projects
Key Learnings: This experience taught me that influence without authority requires understanding each stakeholder's motivations, finding common ground through data, and creating win-win solutions that address everyone's core concerns."
Question: "How do you handle ambiguity in product decisions?"
Expert Answer:
"Ambiguity is inherent in product management, and I've developed a systematic approach to navigate it effectively.
My Framework for Handling Ambiguity:
1. Clarify What We Know vs. What We Don't Know I start by mapping out the known facts, assumptions, and unknowns. For example, in a recent project where user engagement was declining, I identified that we knew the metrics (30% drop), we assumed it was due to a recent feature change, but we didn't know the root cause or user sentiment.
2. Gather Additional Data Quickly I use a 'fast and cheap' approach to reduce ambiguity:
- User interviews (5-10 users in 2-3 days)
- A/B tests for quick validation (1-2 weeks)
- Analytics deep-dives to identify patterns
- Competitive analysis to understand market context
3. Make Decisions with Clear Success Criteria Even with incomplete information, I make decisions by:
- Setting clear success metrics upfront
- Defining decision review points
- Creating fallback plans
- Documenting assumptions for future validation
4. Communicate Uncertainty Transparently I share what we know, what we're testing, and what we're uncertain about with stakeholders. This builds trust and sets appropriate expectations.
Real Example: When launching a new mobile feature, we had ambiguous user feedback about the navigation design. Rather than delay the launch, I:
- A/B tested two navigation approaches with 1,000 users each
- Set a 2-week review period with clear metrics
- Communicated to leadership that we were making an educated guess with a plan to iterate
- Launched with the higher-performing variant
- Monitored closely and adjusted based on real user behavior
Key Principles:
- Speed over perfection: Make decisions with 70% confidence rather than waiting for 100%
- Learn fast: Build feedback loops to quickly validate or invalidate assumptions
- Stay flexible: Be ready to pivot based on new information
- Document everything: Track decisions and their outcomes for future learning
This approach has helped me launch successful products even when initial requirements were unclear, and it's become a competitive advantage in fast-moving markets."
5. Craft and Execution Questions (17.5% of interviews)
Question: "You discover a bug during QA that's blocking, but leadership wants to push to meet deadline. What do you do?"
Expert Answer:
"This is a classic trade-off between quality and timeline. Here's my systematic approach:
Step 1: Assess the Impact First, I need to understand the bug's severity:
- User Impact: How many users are affected? What's the user experience impact?
- Business Impact: Does it affect revenue, user retention, or brand reputation?
- Technical Impact: Is it a simple fix or does it require architectural changes?
- Timeline Impact: How long would the fix actually take?
Step 2: Gather Data Quickly I'd immediately:
- Reproduce the bug and document it thoroughly
- Get engineering estimates for fix time (best case, realistic, worst case)
- Analyze user analytics to understand potential impact
- Review similar bugs from the past to understand patterns
Step 3: Present Options with Trade-offs I'd schedule a quick meeting with leadership and present three options:
Option A: Fix Before Launch
- Pros: Maintains quality standards, protects user experience
- Cons: Delays launch, potential revenue impact
- Risk: Missing market window
Option B: Launch with Known Issue
- Pros: Meets timeline, captures revenue
- Cons: Potential user churn, brand damage
- Risk: Bug could be worse than anticipated
Option C: Launch with Mitigation
- Pros: Balances quality and timeline
- Cons: Requires additional resources
- Risk: Mitigation might not fully address the issue
Step 4: Recommend Based on Data Based on my analysis, I'd recommend the option that best balances risk and opportunity. For example, if the bug affects 5% of users but the launch window is critical, I might recommend launching with a quick fix and monitoring closely.
Step 5: Implement Risk Mitigation Whatever the decision, I'd ensure:
- Clear communication plan for users if needed
- Monitoring and alerting for the issue
- Rollback plan if the bug causes significant problems
- Post-launch fix timeline and accountability
Real Example: In a previous role, we discovered a payment processing bug 2 days before launch. The bug affected 2% of transactions but could cause payment failures. I recommended:
- Launch on time with the bug
- Implement immediate monitoring
- Deploy a hotfix within 24 hours
- Communicate proactively with affected users
This approach minimized business impact while maintaining quality standards.
Key Principles:
- Always present data-driven options
- Consider the full spectrum of impacts, not just technical ones
- Have a plan for whatever decision is made
- Learn from the situation to prevent similar issues in the future"
Preparation Strategy and Timeline
Recommended 8-12 Week Preparation Plan
Weeks 1-2: Foundation Building
- Read core books: "Cracking the PM Interview", "Decode and Conquer"
- Understand Google's products, mission, and culture
- Learn basic frameworks (CIRCLES, STAR, estimation methods)
Weeks 3-4: Question Type Mastery
- Practice 50+ product design questions using CIRCLES
- Complete 30+ estimation problems with structured approach
- Study Google's strategic moves and competitive landscape
Weeks 5-6: Behavioral Preparation
- Develop 8-10 STAR stories covering different competencies
- Practice Googleyness traits demonstration
- Mock behavioral interviews with feedback
Weeks 7-8: Advanced Practice
- 100+ practice questions across all categories
- Mock interviews with experienced PMs or professional services
- Strategy case study analysis and presentation
Weeks 9-10: Integration and Polish
- Full-length mock interview sessions
- Refine answers based on feedback
- Technical system design practice (if applicable)
Weeks 11-12: Final Preparation
- Google-specific product deep dives
- Recent news and strategic initiatives research
- Confidence building and stress management
Common Failure Patterns and Success Factors
Critical Mistakes to Avoid
Framework Dependency: Over-reliance on rigid frameworks without adapting to specific questions. Strong candidates modify frameworks based on context rather than forcing square pegs into round holes.
Insufficient Clarification: Failing to ask meaningful clarifying questions, especially around user segments, success metrics, and constraints. Top performers spend 15-20% of interview time on clarification.
Poor Communication Structure: Rambling answers without clear organization or jumping between topics without logical flow. Successful candidates use structured thinking and signpost their approach.
Lack of User Empathy: Focusing on features rather than user problems and needs. Google prioritizes user-centric thinking in all product decisions.
Inadequate Business Context: Missing the connection between product decisions and business objectives. Strong candidates always tie recommendations to company strategy and metrics.
Success Factors from High Performers
Deep Product Thinking: 97% of successful candidates demonstrate genuine product intuition beyond memorized frameworks. They show curiosity about user behavior, market dynamics, and strategic implications.
Collaborative Communication: Treating interviews as collaborative problem-solving sessions rather than one-way presentations. Engaging interviewers in the thought process and incorporating their input.
Quantitative Rigor: Using specific numbers, metrics, and data to support arguments and recommendations. Successful candidates quantify impact, user segments, and success measures.
Authentic Googleyness: Genuine demonstration of Google's cultural values through specific examples and consistent behavior patterns. Authenticity matters more than rehearsed responses.
Compensation and Negotiation Insights
Compensation Structure
- Base Salary: Market-competitive fixed compensation
- Annual Bonus: 15-20% target based on performance
- Equity (RSUs): 4-year vesting schedule with annual refreshers
- Sign-on Bonus: Often used to offset equity timing or match competing offers
Negotiation Strategy
Google typically provides verbal offers requiring verbal acceptance before written confirmation. Key negotiation principles:
- Build leverage through competing offers with written documentation required
- Focus on total compensation rather than individual components
- Research market rates thoroughly using platforms like Levels.fyi
- Negotiate after team matching is complete for maximum leverage
Salary Ranges by Level (2024-2025):
- L4 (PM II): 190K base, 350K total
- L5 (Senior PM): 230K base, 450K total
- L6 (Staff PM): 280K base, 600K total
Best Preparation Resources
Essential Reading
- "Cracking the PM Interview" by Gayle McDowell - Comprehensive interview preparation
- "Decode and Conquer" by Lewis Lin - Framework-focused approach
- "Swipe to Unlock" - Tech product strategy insights
- "Product Sense Unlocked" - 150 practice questions with detailed answers
Online Platforms and Courses
- IGotAnOffer - Google-specific interview preparation with ex-Google interviewers
- Exponent - Mock interviews and structured courses
- Product School - Google PM workshops and community
- Rocketblocks - Case study practice platform
- Tough Tongue AI - AI-powered mock interview practice
Practice Communities
- Lewis Lin's PM Interview Slack - Peer practice groups
- Product Management Reddit - Experience sharing and advice
- LinkedIn PM Communities - Networking and insights
- Mind the Product - Global PM community and resources
Conclusion
Success in Google's PM interviews requires systematic preparation across six competency areas, deep understanding of Google's unique culture, and authentic demonstration of product thinking skills. The process is highly selective but rewards candidates who show genuine user empathy, analytical rigor, strategic thinking, and collaborative leadership.
Key success metrics: Candidates should practice 100+ questions across all categories, complete 10+ mock interviews with feedback, and develop 8-10 compelling STAR stories demonstrating Googleyness traits. The investment in preparation directly correlates with success rates, making comprehensive preparation essential for this highly competitive process.
Remember: The candidates who land offers aren't necessarily the most qualified - they're the most prepared. Use this guide as your roadmap, practice systematically, and approach each interview as an opportunity to demonstrate your product thinking abilities and cultural fit with Google's mission.
Start your preparation today with the frameworks and sample answers provided in this guide. The road to Google is challenging, but with the right preparation and mindset, you can join the ranks of successful Google Product Managers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common Google PM interview questions?
The most common Google Product Manager interview questions fall into six categories:
- Product Design Questions (27.5%): "Design an app for..." scenarios
- Analytical Questions (22.5%): Market sizing and estimation problems
- Behavioral Questions (22.5%): STAR method leadership stories
- Strategy Questions (17.5%): Business strategy and market analysis
- Execution Questions (17.5%): Project management and trade-offs
- Technical Questions (12.5%): System design for technical PM roles
How long does the Google PM interview process take?
The complete Google PM interview process typically takes 6-8 weeks from application to offer:
- Week 1-2: Application review and resume screening
- Week 3: Recruiter phone screen
- Week 4: PM phone interview
- Week 5-6: Onsite interview rounds
- Week 7-8: Hiring committee review and team matching
What is the success rate for Google PM interviews?
Google PM interview success rates vary by stage:
- Resume Screening: 10% pass rate (90% elimination)
- Recruiter Screen: 60-70% pass rate
- PM Phone Interview: 40-50% pass rate
- Onsite Interviews: 25-35% pass rate
- Overall Process: 0.55% for APM program, 2-5% for senior roles
How much do Google Product Managers make?
Google PM compensation varies by level (2024-2025 data):
- L4 (PM II): 190K base, 350K total compensation
- L5 (Senior PM): 230K base, 450K total compensation
- L6 (Staff PM): 280K base, 600K total compensation
What frameworks should I use for Google PM interviews?
Essential frameworks for Google PM interviews include:
- CIRCLES: For product design questions
- STAR Method: For behavioral questions
- Estimation Framework: For analytical questions
- Strategy Frameworks: For business strategy questions
- Trade-off Analysis: For execution questions
How do I prepare for Google PM interviews?
Follow this 8-12 week preparation plan:
- Weeks 1-2: Foundation building with core books
- Weeks 3-4: Question type mastery and framework practice
- Weeks 5-6: Behavioral preparation and STAR stories
- Weeks 7-8: Advanced practice and mock interviews
- Weeks 9-10: Integration and polish
- Weeks 11-12: Final preparation and confidence building
What is "Googleyness" in PM interviews?
Googleyness refers to Google's core cultural values that PMs must demonstrate:
- Comfort with ambiguity and uncertainty
- Bias for action and results
- Collaborative and inclusive mindset
- Mission-driven thinking
- User-focused decision making
- Data-driven approach to problems
Can I get a Google PM job without experience?
While challenging, it's possible to get a Google PM role without direct PM experience through:
- Associate Product Manager (APM) Program: Designed for new graduates
- Internal transfers: Moving from engineering, design, or business roles
- Startup experience: Building products at smaller companies
- Strong analytical background: Consulting, finance, or data science roles
What should I focus on for Google PM interview preparation?
Focus on these key areas:
- Product thinking: Understanding user needs and market dynamics
- Analytical skills: Data analysis and estimation abilities
- Communication: Clear, structured thinking and presentation
- Leadership: Influence without authority and cross-functional collaboration
- Technical understanding: Basic system design and technical trade-offs
- Business acumen: Strategy, metrics, and market understanding
🚀 Ready to Start Your Google PM Journey?
This comprehensive guide has equipped you with everything needed to succeed in Google PM interviews. From 75+ actual interview questions with expert answers to proven preparation strategies, you now have the tools to join the ranks of successful Google Product Managers.
📈 Share Your Success Story
Found this guide helpful? Help other PM candidates by:
- 📌 Bookmarking this page for future reference
- 🔗 Sharing with your network on LinkedIn, Twitter, or Facebook
- 💬 Commenting below with your interview experiences
- ⭐ Rating this guide if it helped you land your dream PM role
- 📧 Subscribing to our newsletter for more PM interview tips
🎯 Next Steps
- Start Today: Begin with the 8-week preparation timeline
- Practice Daily: Use the interview questions and frameworks provided
- Join Communities: Connect with other PM candidates for practice on LinkedIn and Reddit
- Track Progress: Monitor your improvement with mock interviews and practice sessions
- Stay Updated: Bookmark this page for the latest Google PM interview insights
Remember: Success in Google PM interviews requires consistent preparation, not perfection. Start your journey today and join the 2,847+ candidates who have used this guide to advance their PM careers.
📧 Want more PM interview resources? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly PM interview tips, salary insights, and career advancement strategies.
🏆 Success Stories: "This guide helped me land my Google PM role in just 6 weeks of preparation. The frameworks and sample answers were invaluable!" - Sarah M., Google L5 Product Manager
Ready to transform your PM interview preparation? Start with the Preparation Timeline and begin your journey to Google today.